Rev 2 1 7 02 2020 tensile stress mpa strain 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 0 0 02 0 04 0 06 0 08 0 10 mim 1 ph ss rouht 1 ph ss marore 1 ph ss all data and graphs on front page reflect values of h900 heat treated 17 4 ph ss.
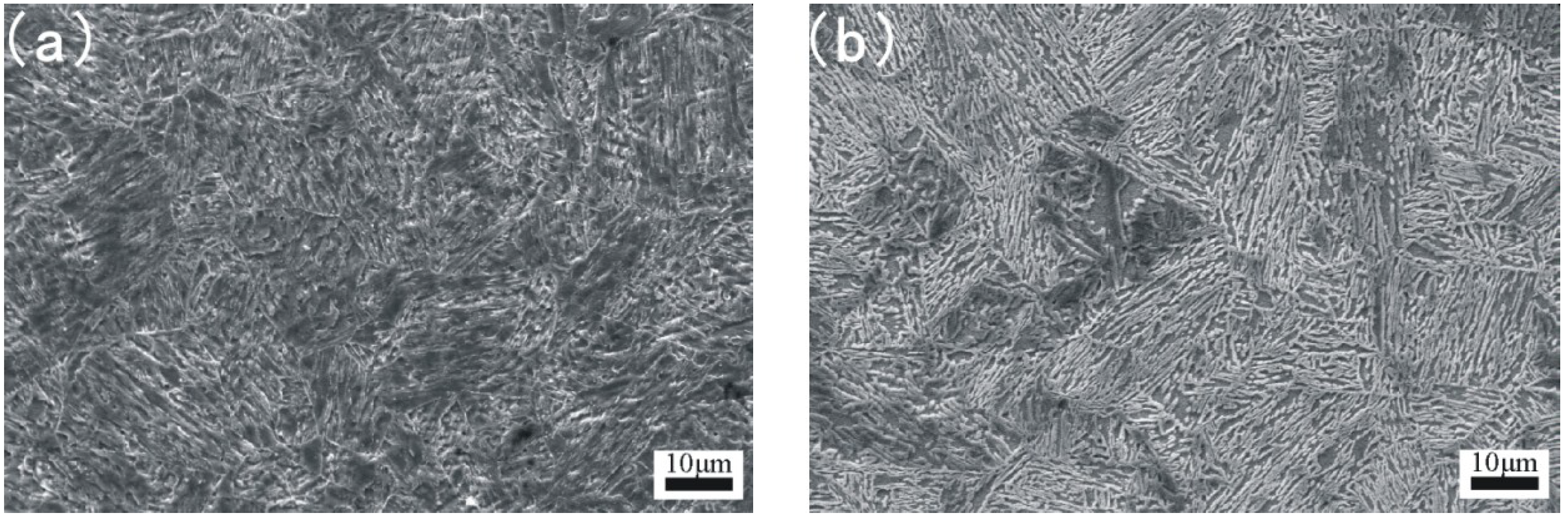
17 4 stainless steel microstructure.
Wang j zou h li c peng yh qiu s shen b.
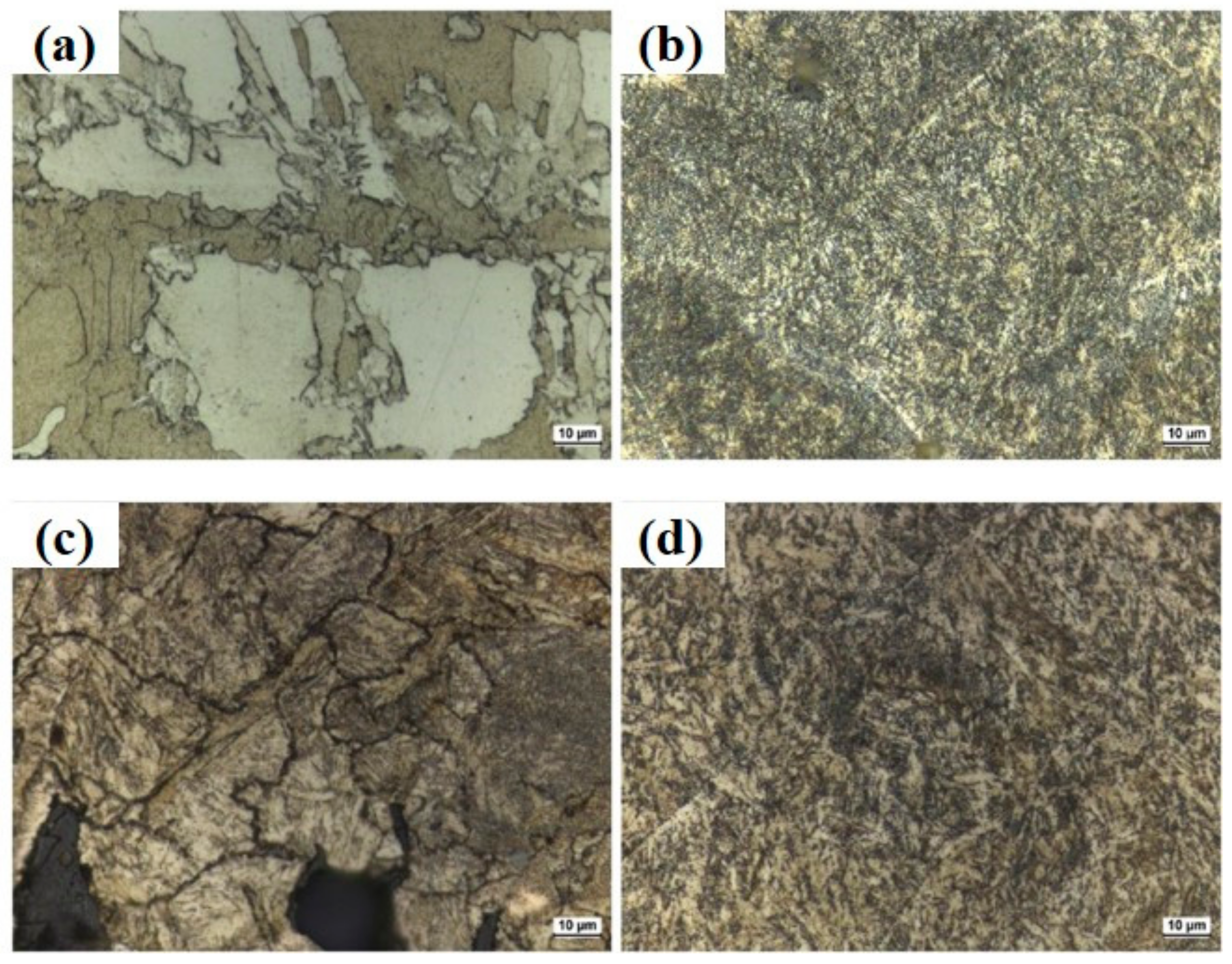
The microstructure of 17 4 ph stainless steel at various stages of heat treatment i e after solution heat treatment tempering at 580 c and long term aging at 400 c have been studied by.
17 4 ph mim standard stainless steel heat treated to h900 specification.
Hardening is achieved by a short time simple low temperature treatment.
J chem phys 1972.
As the homogenizing treatment time increased the length of δ.
Materials science and engineering a 1988.
It is further strengthened by a low temperature treatment which precipitates a copper containing phase in the alloy.
Effects of aging on the 13.
In gen eral the corrosion resistance of al 17 4 alloy is supe rior to that of the hardenable 400 series stainless steels.
While the powder used was gas atomized 17 4ph stainless steel with a.
Al 17 4 precipitation hardening alloy is comparable to that of type 304 stainless steel in most media.
As with other precipitation hardening alloys al 17 4 pre cipitation hardening alloy is more susceptible to stress.
The microstructure and microhardness of the laser ss processed part will be analyzed.
The microstructure evolution of usr treated 17 4ph stainless steel and the surface modification layer were observed and analyzed in detail.
Structure evolution of type 17 4 ph stainless steel during long term aging at.
Xperimental m ethod the substrate used in this research was 316 stainless steel coupons with dimension of 100 100 10 mm.
The microstructures and mechanical properties of 17 4 ph stainless steel at each steps of heat treatment such as homogenizing solid solution treatment followed by aging treatment longterm aging at 400 c and recovery treatment in order to obtain a better understanding of the embrittlement phenomena on aging was investigated.
Unlike conventional martensitic stainless steels such as type 410 17 4 is quite weldable.
Produced 17 4ph stainless steel ss parts.
Viswanathan r banerjee s krishnan r.
It includes the addition of chromium nickel copper and niobium making it a truly martensitic microstructure.
High strength 17 4 ph stainless steel with a higher chromium content than 15 5 ph stainless steel this high strength 17 4 ph offers better corrosion resistance.
Markforged represent typical tested values.
Microstructure of 17 4 ph stainless steel.
It is also known as 630 stainless steel.